Before talking about some characteristics of the Delta Tocotrienol, it is necessary to describe those of the vitamin from which this derives: Vitamin E.
Vitamin E, also known as Tocopherol, is a fat soluble vitamin that mammals, including humans, introduce into the body through food. It is accumulated in the liver and therefore it is not necessary to take it daily. The body releases it in small doses when its use becomes necessary.
Of all the vitamins, it is certainly the most common. Its remarkable antioxidant and anti-free radical properties have been scientifically demonstrated, as well as its ability to promote cell renewal. These features make it an important cancer prevention tool.
Vitamin E is sensitive to heat and light, therefore it tends to degrade in the presence of high temperatures or when it is exposed to light rays.
It is widespread in food, especially in oily fruits (such as olives, peanuts, corn) and in wheat seeds. It is also found in cereals, nuts and green leafy vegetables.
The daily requirement of vitamin E is around 8-10 mg.
The deficiency of vitamin E, or tocopherol, can generally occur when a situation of malnutrition occurs, while taking unbalanced diets or in the course of malabsorption. In younger subjects it can cause defects in growth and development. In general, the lack of vitamin E can be the basis for the onset of nervous system disorders.
The excess of vitamin E, or tocopherol, is quite rare. When it occurs it can have negative consequences due to the consequent rise in blood pressure and which can be dangerous for those who already suffer from hypertension.
An excess of vitamin E can also create problems for those suffering from thyroid gland, since it can reduce the hormones of this gland. Other consequences of excess vitamin E can be widespread fatigue, digestive disturbances, nausea and vomiting.
Vitamin E has important anti-tumor functions thanks to its powerful antioxidant action that allows it to protect cell membranes and to directly intervene on particular transcription factors used by cancer cells to proliferate. But this vitamin assumes an important role also in relation to pathologies of cardiovascular origin, being able to reduce the phenomena of platelet aggregation with consequent reduction of the formation of emboli, plaques and thrombi in the arteries.
Vitamin E is also a valuable anticoagulant because it prevents excessive blood coagulation without however preventing the normal coagulation required in case of wounds, useful to stop a bleeding. Finally, vitamin E allows you to reduce your cardiovascular risk thanks to the fact that with its action the level of the so-called good cholesterol increases at the expense of the "bad" one.
From a biochemical point of view, this vitamin is actually made up of two subgroups of molecules, tocopherols and tocotrienols. In turn, each of these two subgroups is divided into four isoforms: alpha, beta, delta and gamma.
Each of these isoforms, when isolated, maintains the same virtues as the whole complex, in many cases the isolation of an isoform greatly amplifies its qualities and characteristics.
Among these isoforms, the Delta-tocotrienol it is probably the most studied in the context of oncological pathologies. Tocotrienols, according to the data of the scientific literature, are those that have positive effects on different aspects of human health (anti-inflammatory action, prevention of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, etc.). Some in vitro and preclinical studies have shown that δ-TT (delta-tocotrienol) is the most active tocotrienol in counteracting the proliferation of human melanoma cells.
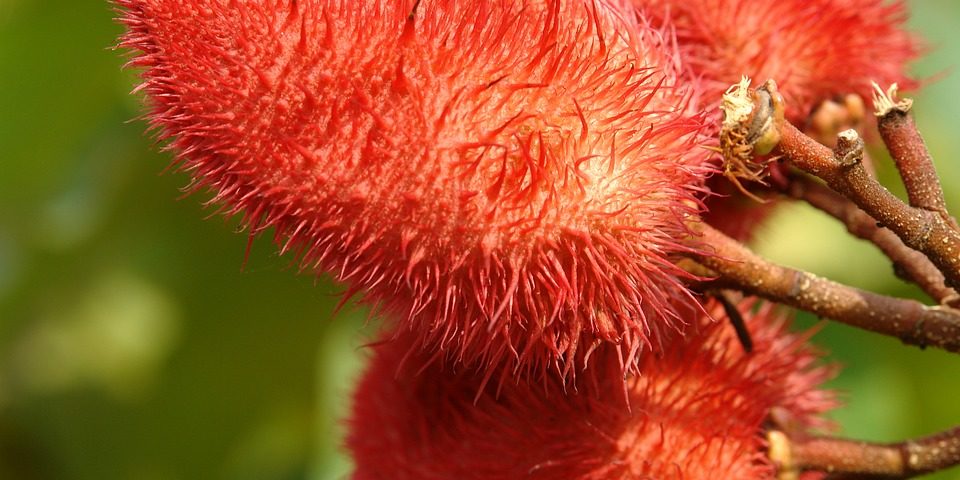
Tocotrienols are found in high concentrations in unrefined palm oil (the 50% of the vitamin E compound extract is made up of δ-TT and γ-TT) but also and mostly in Annatto seeds (Bixa Orellana; 99% of δ-TT).
Bixa orellana
The information contained on the Site, in the various articles, in the contents, in any responses to comments, are for informational purposes only and in no way have the claim or purpose of replacing the opinion of the doctor and / or specialist, of others. health professionals or professionals in the sector who must in any case be contacted and consulted for the formulation of a diagnosis or the indication of a possible correct therapeutic and / or dietary and / or food supplement program, and more generally for the comparison on this information. In no case will the Site, the Publisher who manages it, the authors of the articles and / or contents and / or comments and / or blogs, or other subjects connected to the Site, be responsible for any damage, even if only hypothetically connected. the use of the contents and / or information present on the Site. The Site assumes no responsibility for the misuse that users may make of the information contained in the Site.